Opinion: We need to save languages as well as species | reviews, news & interviews
Opinion: We need to save languages as well as species
Opinion: We need to save languages as well as species
Should the dying of languages be one of the 21st century's big causes?
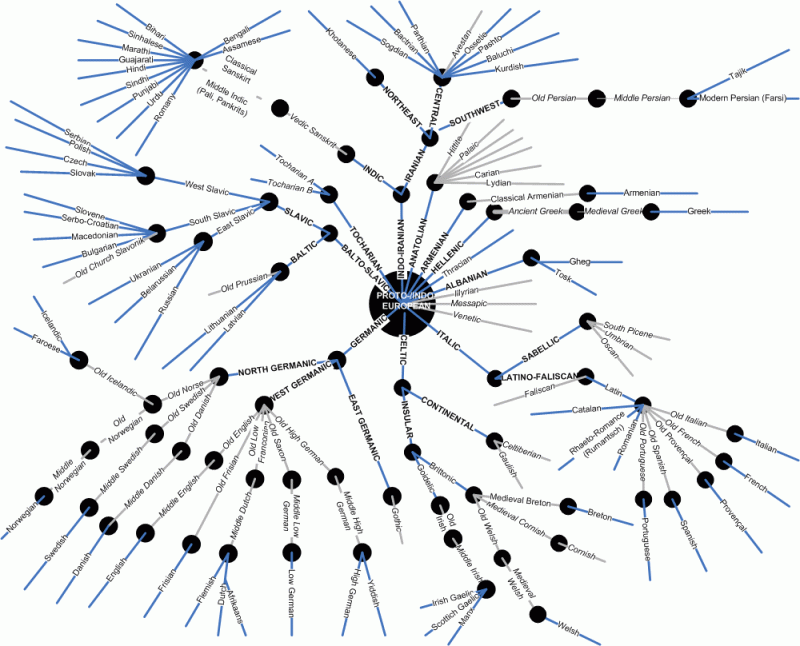
In the past few decades we've all learnt to pay at least lip service to ecological matters, and millions of people in this country are members of environmental organisations. But perhaps we should also focus our attention on an issue that could be one of the big causes of the 21st century - the disappearance of languages.
While estimates suggest that in the next 100 years perhaps five per cent of species will be wiped out, languages are under as much or more threat. The consensus (Mark Abley's book Spoken Here: Travels Among Threatened Languages, for example) seems to be that on current trends, between 50 and 90 per cent of the world's 6,000 or so languages will cease to exist over the next century.
Should we care? If everyone spoke the same language, wouldn't we all be able to communicate with each other better? My grandmother campaigned for that great lost cause Esperanto, a utopian global language. With English the language of technology and commerce, and with only Chinese and Spanish serious rivals, we might even feel a glow of chauvinism about our triumphant tongue.
If ecologists have taught us anything, it's that monoculture is not just boring, but dangerous. But languages are beautiful, complex living things, and the world will be hugely impoverished if so many are wiped out. As each language disappears, so does knowledge built up over centuries, some of which may be useful to the world. It's like the burning of the library at Alexandria, which destroyed most of the learning of the ancient world.
Most people would accept the argument for conserving unstudied endangered plants – they might, for example be medically useful – but the local language that explains the use of Amazonian herbs, for example, is also highly valuable. As Andrew Woodfield of the Centre for Theories of Language in Bristol puts it, "By allowing languages to die out, the human race is destroying things it doesn't understand."
Certainly languages embody radically different world-views. English pronouns, for example, are impoverished compared to many languages. In Abley’s book he comes across one Aboriginal language, Murrinh-Patha, which has at least eight words for "they". As a result, "you have to keep human relationships in mind all the time. It's as though the language requires you to think in certain ways."
We know, and Kate Bush has just reminded us, that the Inuits have many words for snow; more impressive is that they also have numerous words for "know", including words for "knowing from experience" and "being no longer unaware". Such subtleties can be highly poetic. Among the Boro, an endangered language from north-eastern India, "onguboy" means to love from the heart, "onsay" means to pretend to love, while "onsra" means to love for the last time.
Abley also has some splendidly wacky encounters, such as the last two surviving speakers of an Aboriginal language who are forbidden by tribal taboos from talking to each other, and the last surviving speaker of one Amazonian language – a parrot.
My interest in this subject comes from being a writer on world music, where it is clear that many types of music are endangered by globalisation. The destruction of language leads to the extinction of many cultural forms, and if ecologists have taught us anything, it's that monoculture is not just boring, but dangerous. A farm with only one crop is more vulnerable to disease.
Of course, there will be some species and languages that die out in an evolving world. That's the natural way of things. But the unprecedented speed of extinction is the worrying new aspect.
Cultures that become moribund have always been revitalised by outside influences. The Renaissance was started by translations of texts from the Classical world and Arabic discoveries in mathematics, medicine and astronomy. In the 19th century, most Europeans would have been puzzled to think that we might have learnt from African culture. Yet in the past century its influence on everything from art to music has been immense.
Already there are signs of our culture turning into a self-referring loop (endless TV about TV, for example). But if the languages containing alien concepts that might revitalise us disappear, we will surely stagnate. With only the odd Amazonian parrot to remind us that there is more than one way of looking at the world.
Add comment
The future of Arts Journalism
You can stop theartsdesk.com closing!
We urgently need financing to survive. Our fundraising drive has thus far raised £49,000 but we need to reach £100,000 or we will be forced to close. Please contribute here: https://gofund.me/c3f6033d
And if you can forward this information to anyone who might assist, we’d be grateful.

Subscribe to theartsdesk.com
Thank you for continuing to read our work on theartsdesk.com. For unlimited access to every article in its entirety, including our archive of more than 15,000 pieces, we're asking for £5 per month or £40 per year. We feel it's a very good deal, and hope you do too.
To take a subscription now simply click here.
And if you're looking for that extra gift for a friend or family member, why not treat them to a theartsdesk.com gift subscription?
more
 'We are bowled over!' Thank you for your messages of love and support
Much-appreciated words of commendation from readers and the cultural community
'We are bowled over!' Thank you for your messages of love and support
Much-appreciated words of commendation from readers and the cultural community
 Scott, Irish Baroque Orchestra, Whelan, RIAM, Dublin review - towards a Mozart masterpiece
Characteristic joy and enlightenment from this team, but a valveless horn brings problems
Scott, Irish Baroque Orchestra, Whelan, RIAM, Dublin review - towards a Mozart masterpiece
Characteristic joy and enlightenment from this team, but a valveless horn brings problems
 Music Reissues Weekly: The Earlies - These Were The Earlies
Lancashire and Texas unite to fashion a 2004 landmark of modern psychedelia
Music Reissues Weekly: The Earlies - These Were The Earlies
Lancashire and Texas unite to fashion a 2004 landmark of modern psychedelia
 Hamlet, National Theatre review - turning tragedy to comedy is no joke
Hiran Abeyeskera’s childlike prince falls flat in a mixed production
Hamlet, National Theatre review - turning tragedy to comedy is no joke
Hiran Abeyeskera’s childlike prince falls flat in a mixed production
 Like Water for Chocolate, Royal Ballet review - splendid dancing and sets, but there's too much plot
Christopher Wheeldon's version looks great but is too muddling to connect with fully
Like Water for Chocolate, Royal Ballet review - splendid dancing and sets, but there's too much plot
Christopher Wheeldon's version looks great but is too muddling to connect with fully
 Lee Miller, Tate Britain review - an extraordinary career that remains an enigma
Fashion photographer, artist or war reporter; will the real Lee Miller please step forward?
Lee Miller, Tate Britain review - an extraordinary career that remains an enigma
Fashion photographer, artist or war reporter; will the real Lee Miller please step forward?
 Rohtko, Barbican review - postmodern meditation on fake and authentic art is less than the sum of its parts
Łukasz Twarkowski's production dazzles without illuminating
Rohtko, Barbican review - postmodern meditation on fake and authentic art is less than the sum of its parts
Łukasz Twarkowski's production dazzles without illuminating
 Lee, Park Theatre review - Lee Krasner looks back on her life as an artist
Informative and interesting, the play's format limits its potential
Lee, Park Theatre review - Lee Krasner looks back on her life as an artist
Informative and interesting, the play's format limits its potential
 Ariodante, Opéra Garnier, Paris review - a blast of Baroque beauty
A near-perfect night at the opera
Ariodante, Opéra Garnier, Paris review - a blast of Baroque beauty
A near-perfect night at the opera
 Classical CDs: Voice flutes, flugelhorns and froth
Baroque sonatas, English orchestral music and an emotionally-charged vocal recital
Classical CDs: Voice flutes, flugelhorns and froth
Baroque sonatas, English orchestral music and an emotionally-charged vocal recital
 Odd times and clunking lines in 'The Life of a Showgirl' for Taylor Swift
A record this weird should be more interesting, surely
Odd times and clunking lines in 'The Life of a Showgirl' for Taylor Swift
A record this weird should be more interesting, surely

Comments
Peter Culshaw wrote, "My
Esperanto is no lost cause.
I use Esperanto every day to
Have to say the advantage of
Have to say the advantage of a comment section is that it can be informative, and I realse that Esperanto is still very much a going concern.
People should realise that