Gerhard Richter: Panorama, Tate Modern | reviews, news & interviews
Gerhard Richter: Panorama, Tate Modern
Gerhard Richter: Panorama, Tate Modern
A solid and interesting survey of the German artist, rather than a brilliant and thrilling one

In recent years it seems we have seen an awful lot of Gerhard Richter. There have been three major exhibitions in London well within the last seven or eight years. One is hardly complaining, since there is always a demand to see “the world’s most influential living painter”, as he is often claimed to be (and not without some reason).
But Richter’s practice is characterised by its mastery of several genres and many styles: it takes us from small photorealist portraits to giant monochrome abstract canvases, from homely landscapes in 19th-century style to blurred black-and-white images that imitate the look of smudgy newspaper print.
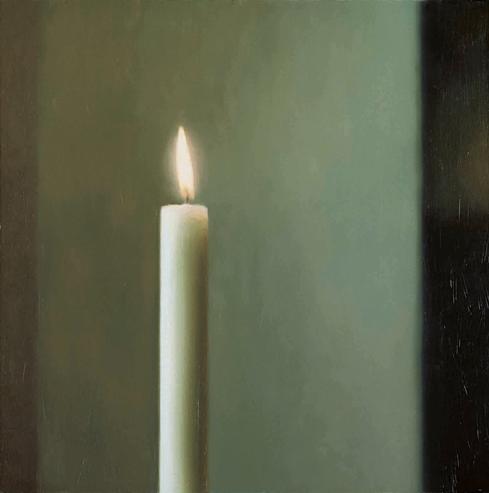 Tate Modern’s survey is the first full retrospective of the German artist since the last one at Tate Gallery 20 years ago. In that exhibition, Richter’s homage to German Romanticism and the Sublime – the roiling, grey seascapes and the intense, quietly powerful, part Catholic, part Zen candle paintings (Candle, pictured right) – are the encounters I remember with most clarity. But they hardly make anything like the impression they made then. Familiarity is partly to blame, of course (the seductive first encounter that initiated a question: who else is painting like this now?) and possibly the fact that here they are not given a room to themselves but are juxtaposed, as are most of the figurative works here, with large-scale abstract paintings in this loosely chronological hang.
Tate Modern’s survey is the first full retrospective of the German artist since the last one at Tate Gallery 20 years ago. In that exhibition, Richter’s homage to German Romanticism and the Sublime – the roiling, grey seascapes and the intense, quietly powerful, part Catholic, part Zen candle paintings (Candle, pictured right) – are the encounters I remember with most clarity. But they hardly make anything like the impression they made then. Familiarity is partly to blame, of course (the seductive first encounter that initiated a question: who else is painting like this now?) and possibly the fact that here they are not given a room to themselves but are juxtaposed, as are most of the figurative works here, with large-scale abstract paintings in this loosely chronological hang.
These juxtapositions present a powerful dialogue (primarily about the plasticity of paint), but as for the abstract works themselves, as varied in colour and in texture as many of them are, they eventually begin to feel like punctuations rather than further insights into Richter’s practice. There are, for instance, too many squeegee paintings – wet paint that has been rolled with a squeegee, creating striations, strips and blots of different hues and surface textures. Some of these, like the Forest series of the early 1990s, are rather arresting when encountered as a series: we see bright vertical marks of yellow or orange against layered blue grounds, which vaguely resemble vibrating sound waves turned on their sides. Richter remains deeply interested in the effects of chance, an inheritance from the early Modernists.
Moving through the exhibition (curated by Nicholas Serota and Tate curator Mark Godfrey), one becomes acutely aware that one is being earnestly guided to focus on the full range of processes and techniques at Richter’s disposal, rather than becoming merely absorbed in a search for meaning through subject and narrative - which is far more likely to happen with a thematic hang, of which Tate is usually so fond. Richter is a virtuoso, for sure, but I think this is exactly the kind of mixing, disruption and repetition that does Richter few favours.
Many of the early paintings confront Germany’s recent history and are intimately linked to Richter’s family history
This exhibition is bigger than the one two decades ago, but still feels somehow incomplete. And this makes it a solid and interesting survey, rather than a brilliant and thrilling one. Now 80, Richter’s career has been long and productive, so what to leave out and what to put in is inevitably going to create interesting problems. But if one is at all broadly familiar with Richter’s work, one may still miss a few key pieces. His painting of a distressed Jackie Kennedy, reeling from the shock of the assassination of her husband, is undoubtedly one of his most powerful portraits. But it doesn’t make an appearance. Nor do any of his related series of American political paintings.
His most famous and justly celebrated portraits do, of course: Betty (1988) (main picture), whose face is tantalisingly and eternally denied us, and the equally photographic Reader (1994), after a painting by Vermeer. But how much do we really need to see a failed painting of a copy of a Titian (Annunciation after Titian, 1973), so smooth and bright and kitsch? Or all three of his massive cloud paintings, each a depiction of a single cloud in a grey-blue sky - minus, one can imagine, the accompanying angels and cherubs?
 Many of the early paintings from the late Sixties confront Germany’s recent history and are intimately linked to Richter’s family history. These look back from a distance of 30-odd years from the original photographs on which the images are based. Two blurry greyscale paintings from 1965, Aunt Marianne (pictured left) and Uncle Rudi, are taken from family photos. A smiling girl, the picture of Aryan girlhood if you will, is tending a restive baby (Gerhard); later, suffering from mental illness, Marianne was forced to undergo sterilisation under the Nazi regime, then eventually killed. Uncle Rudi, meanwhile, smiles broadly for the camera in his dashing Wermstang overcoat. But he too will soon be dead, killed in battle within the first few weeks of the start of war.
Many of the early paintings from the late Sixties confront Germany’s recent history and are intimately linked to Richter’s family history. These look back from a distance of 30-odd years from the original photographs on which the images are based. Two blurry greyscale paintings from 1965, Aunt Marianne (pictured left) and Uncle Rudi, are taken from family photos. A smiling girl, the picture of Aryan girlhood if you will, is tending a restive baby (Gerhard); later, suffering from mental illness, Marianne was forced to undergo sterilisation under the Nazi regime, then eventually killed. Uncle Rudi, meanwhile, smiles broadly for the camera in his dashing Wermstang overcoat. But he too will soon be dead, killed in battle within the first few weeks of the start of war.
Richter was born in Dresden in 1932, and the destruction of that city, and the ruination of other European townscapes, is another early theme. We see swarms of fighter aircraft, like Airfix models dispensing tiny pellets, and paintings of greyly indistinct rubble, which turn out to be topographical studies.
Distrusting what our eyes tell us is a key Richter concern
Often Richter’s gaze seems pitiless and cold, but perhaps not always. In an image of his father, with whom he had almost no relationship, we see an old man with his hair in two tufty points that echo the ears of the small, button-eyed dog he is carrying. He looks utterly ridiculous and yet we see the pity of it, the aching vulnerability in his round-eyed, bemused gaze. Later the Baader-Meinhof gang, in a series of black-and-white paintings painted just over a decade after their deaths in custody, are shown in a room by themselves, the only series given a room of their own. Do we detect empathy here, too?
And sometimes Richter plays with double illusions: a car speeds past in a grey blur, but the trees en route are also depicted in a speed-blur – we cannot trust what we are seeing in relation to ourselves, for a moving object amid stationary objects are both given the same blurry treatment. Indeed, distrusting what our eyes tell us is a key Richter concern. September, painted in 2005, four years after 9/11, shows one of the twin towers about to be hit. But the blurry fragments only coalesce in this apparently abstract image when we read the background information accompanying the image.
In the end, this is an exhibition that shows us what an assured and supreme virtuoso Richter is, but it also shows us weaknesses. This rounded view may be a very good thing (however venerated, Richter is human, after all). But a fuller retrospective would surely not have denied us a few more of the greats. And perhaps it would not have allowed so many of the (clearly) lesser abstracts.
- Gerhard Richter: Panorama at Tate Modern until 8 January, 2012
Explore topics
Share this article
more Visual arts
 Stephen review - a breathtakingly good first feature by a multi-media artist
Melanie Manchot's debut is strikingly intelligent and compelling
Stephen review - a breathtakingly good first feature by a multi-media artist
Melanie Manchot's debut is strikingly intelligent and compelling
 Fantastic Machine review - photography's story from one camera to 45 billion
Love it or hate it, the photographic image has ensnared us all
Fantastic Machine review - photography's story from one camera to 45 billion
Love it or hate it, the photographic image has ensnared us all
 Yinka Shonibare: Suspended States, Serpentine Gallery review - pure delight
Weighty subject matter treated with the lightest of touch
Yinka Shonibare: Suspended States, Serpentine Gallery review - pure delight
Weighty subject matter treated with the lightest of touch
 Jane Harris: Ellipse, Frac Nouvelle-Aquitaine MÉCA, Bordeaux review - ovals to the fore
Persistence and conviction in the works of the late English painter
Jane Harris: Ellipse, Frac Nouvelle-Aquitaine MÉCA, Bordeaux review - ovals to the fore
Persistence and conviction in the works of the late English painter
 Sargent and Fashion, Tate Britain review - portraiture as a performance
London’s elite posing dressed up to the nines
Sargent and Fashion, Tate Britain review - portraiture as a performance
London’s elite posing dressed up to the nines
 Zineb Sedira: Dreams Have No Titles, Whitechapel Gallery review - a disorientating mix of fact and fiction
An exhibition that begs the question 'What and where is home?'
Zineb Sedira: Dreams Have No Titles, Whitechapel Gallery review - a disorientating mix of fact and fiction
An exhibition that begs the question 'What and where is home?'
 Yoko Ono: Music of the Mind, Tate Modern review - a fitting celebration of the early years
Acknowledgement as a major avant garde artist comes at 90
Yoko Ono: Music of the Mind, Tate Modern review - a fitting celebration of the early years
Acknowledgement as a major avant garde artist comes at 90
 Unravel: The Power and Politics of Textiles in Art, Barbican review - the fabric of dissent
An ambitious exploration of a neglected medium
Unravel: The Power and Politics of Textiles in Art, Barbican review - the fabric of dissent
An ambitious exploration of a neglected medium
 When Forms Come Alive, Hayward Gallery review - how to reduce good art to family fun
Seriously good sculptures presented as little more than playthings or jokes
When Forms Come Alive, Hayward Gallery review - how to reduce good art to family fun
Seriously good sculptures presented as little more than playthings or jokes
 Entangled Pasts 1768-now, Royal Academy review - an institution exploring its racist past
After a long, slow journey from invisibility to agency, black people finally get a look in
Entangled Pasts 1768-now, Royal Academy review - an institution exploring its racist past
After a long, slow journey from invisibility to agency, black people finally get a look in
 Barbara Kruger, Serpentine Gallery review - clever, funny and chilling installations
Exploring the lies, deceptions and hyperbole used to cajole, bully and manipulate us
Barbara Kruger, Serpentine Gallery review - clever, funny and chilling installations
Exploring the lies, deceptions and hyperbole used to cajole, bully and manipulate us
 Richard Dorment: Warhol After Warhol review - beyond criticism
A venerable art critic reflects on the darkest hearts of our aesthetic market
Richard Dorment: Warhol After Warhol review - beyond criticism
A venerable art critic reflects on the darkest hearts of our aesthetic market

Add comment